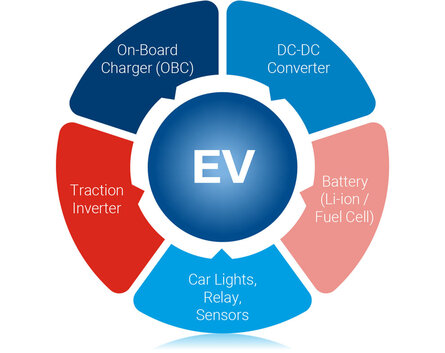
Speeding Up Testing
The electrification of vehicles has expanded beyond consumer passenger cars into commercial and industrial transportation, leading to constant advancements in automotive electronics. While once focused on entertainment, navigation, and comfort systems, the industry now prioritizes high power, high voltage, and energy management systems.
These power requirements aren't limited to just the battery and electric motor, as the drivetrain and power management systems also have similar demands. To keep pace with the rapidly changing needs of electric vehicles, test engineers must stay ahead of trends and avoid frequent replacement of test equipment.
EA Elektro-Automatik GmbH & Co. KG (EA) offers a line of DC power supplies, electronic loads, and bidirectional power supplies that provide the flexibility to test multiple devices and meet future requirements. The PSI, EL, ELR, PSB and PUB series from EA can reach up to 2000V and feature: true auto-ranging, on-board arbitrary waveform and a function generator.
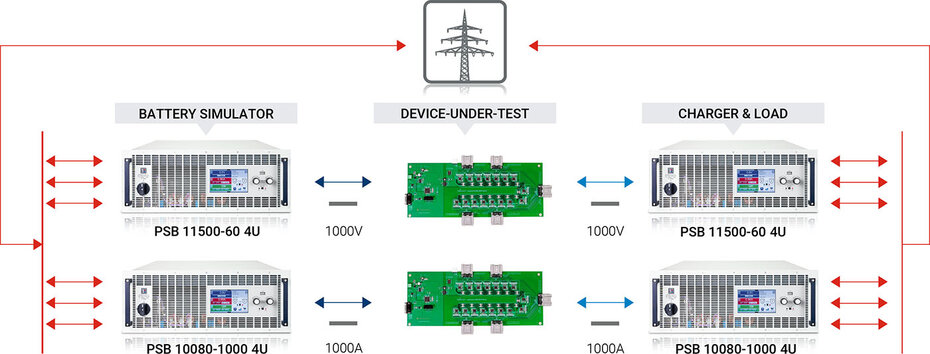
Fuel Cells, Batteries, and Battery Management System Testing
The power source for electric vehicles consists of batteries, or fuel cells, and are managed by a battery management systems in modern vehicles. With the high demand for power throughout the vehicle it is crucial to test batteries and fuel cells by replicating real-world conditions.
From starts and stops to rush hour traffic in scorching heat with the air conditioning on, EVs face various challenges on the road, and the ability to simulate these scenarios is essential to meet automotive testing standards.
To learn more about testing these power sources please refer to the chapters for batteries and fuel cells.
But how to test a battery management system?
That is where Device Under Test (DUT) concepts kick in.
EAs DC power supplies, loads, and bidirectional DC supplies simplify simulation of various driving conditions with their built-in function and arbitrary waveform generator. They also have battery test features that can automatically simulate to charge or discharge a battery.
The bidirectional capability of EA's PSB series enables accurate simulation of a battery, or a battery charger to test battery management systems without the need to wait for a specific state of charge. Furthermore, no specific charging station or battery needs to be aquired. With the help of two bidirectional power supplies battery charger and battery are simulated.
Do you like to find out more? Talk to us. - We would be happy to arrange a meeting, or a seminar appointment.
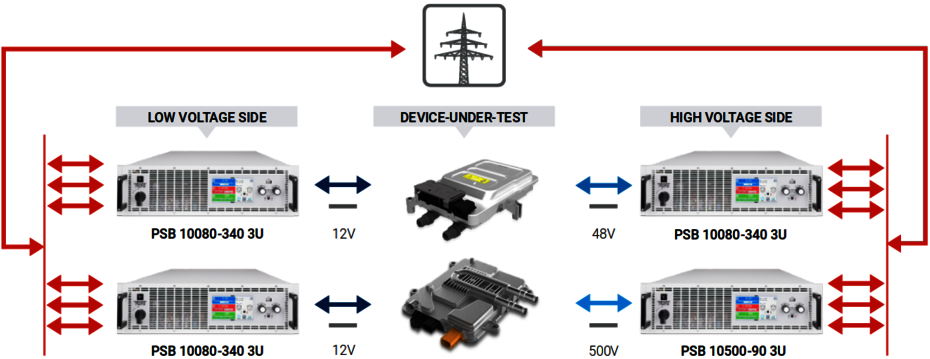
DC-DC Converter Testing
This is another DUT application, but differs from battery management testing since different voltages have to be taken into account.
In electric vehicles, DC to DC converters convert high battery voltages (200-800V) to the low DC voltages (12-48V) needed by the headlights, radio, and other accessories. Testing these converters requires a DC input and a load to connect the DC output. EA's power supplies and loads offer low and high voltage options to meet these needs. EA's bidirectional power supplies, like the PSB 10000 series, can do both source and sink voltage, reducing the amount of test equipment required.
With the built-in function generator, real-world scenarios can be simulated, such as repeatedly turning on and off the headlights or using the heater on full blast in winter. A typical test setup is using a pair of PSBs to test both sides of the DC to DC converter. That is shown in the figure below. The high efficiency of the PSBs means that only 5-10% of the power gets lost during these tests, while the rest of the power being returned to the local power grid.
Do you like to find out more? Talk to us. - We would be happy to arrange a meeting, or a seminar appointment.
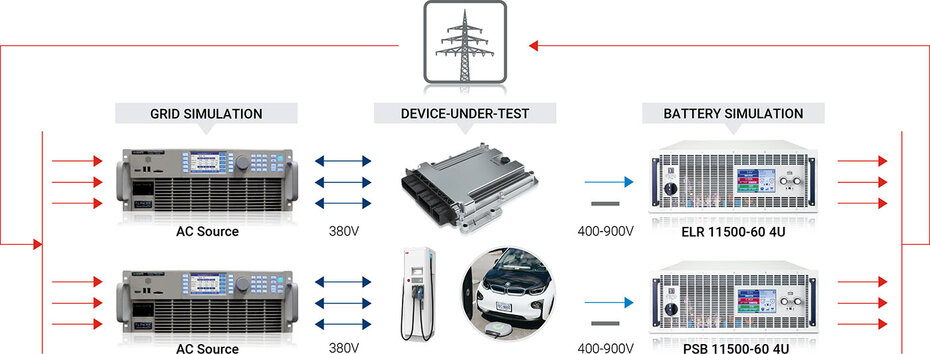
Charge System Testing
Testing of on board chargers, or charging stations
Charger system testing is another DUT application, which differs from all above. For this application different voltage types have to be considered.
A key consideration when buying an electric vehicle is how and where it will be charged. The automotive industry is exploring various charging solutions to minimize the impact on drivers. Charging can be done with a simple ICCPD cable (Mode 2), through an AC wallbox or charging station (Mode 3) or with an Fast DC charger (Mode 4).
EA's regenerative electronic loads (ELR) and bidirectional power supplies are used to simulate the vehicle battery during tests of on-board chargers (Mode 2 and Mode 3), or DC charging stations (Mode 4)
EA's DC power supplies with auto-ranging capability can adapt to these changing needs. Auto-ranging provides full power across a wide voltage range, not just at maximum voltage like traditional DC power supplies. EA also offers high-power density models with voltage ratings of 1000V, 1500V, and 2000V. These models feature bidirectional capability, function generators, regenerative capability, and low EMC emissions, meeting the growing demands of EV charging systems.
To learn more how to built your own Mode 3 charging station please refer to charging technology chapter.
For more informations regarding infrastructure sensors in charging stations like RDC, RCMB or IMD refer to infrastructure sensors.
Do you like to find out more? Talk to us. - We would be happy to arrange a meeting, or a seminar appointment.
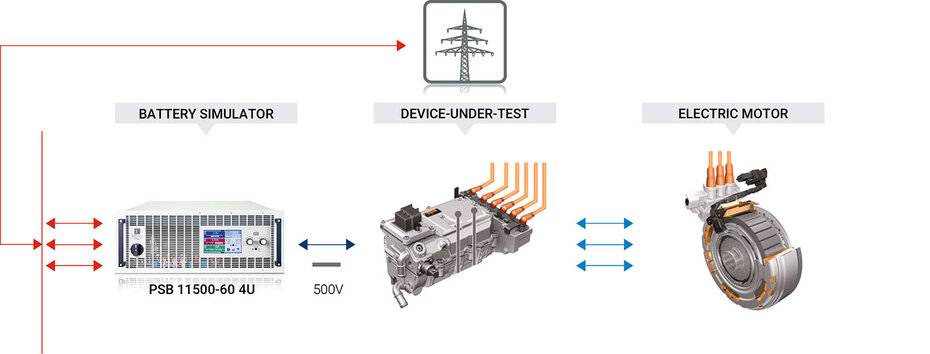
Traction Inverter Testing
In electric vehicles, AC drives the motors while DC power supplies the majority of the components in the vehicle, which is logical considering the source of the power is a battery. Traction inverters are utilized to transform the power back and forth between the battery (DC) and the motor (AC). These inverters also play a role in energy recovery (during braking), increasing voltage, and providing switch protection. As shown below, EA's bidirectional PSB supplies being used to test a traction inverter in connection with an electric motor.
The PSB can supply power to the traction inverter, imitate a battery, and also absorb the energy when the motor operates as a generator during braking and recharging of the battery. The auto-ranging feature of EA provides a more flexible output range compared to traditional DC power supplies, making the full power output available as the voltage output decreases. This means that EA's DC power supplies and loads can substitute for multiple traditional DC supplies that are typically required to cover the various operating points of the traction inverter, including higher voltage/lower current and low voltage/higher current.
Do you like to find out more? Talk to us. - We would be happy to arrange a meeting, or a seminar appointment.
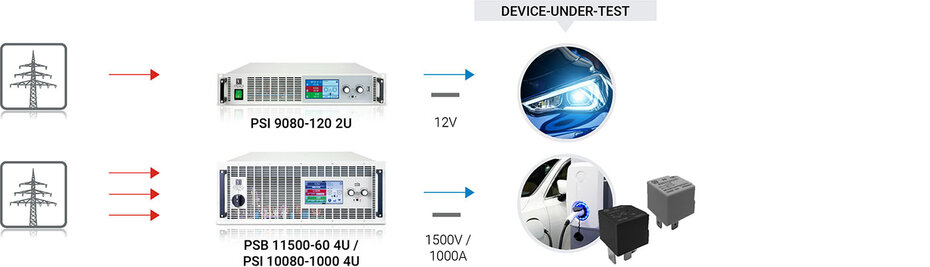
Accessory Testing
As mentioned above, in addition to the key components of electric vehicles, several other components in both EVs and combustion engine vehicles also run on DC power. The voltage requirements to power these components can range from the standard 12V to 1000V or more, making it necessary for test engineers to have multiple traditional DC power supplies for testing purposes. However, EA's DC supplies and loads, with their high power density and auto-ranging capabilities, cover a much wider operating range, saving valuable rack space and reducing costs.
EA's exceptional efficiency can save you huge amount on annual energy costs, floor space, and cooling capacity. Integration into Automatic Test Environment (ATE) is also made easier through the use of Anybus modules for digital communication, offering options such as CANopen, CAN, Ethernet, Profibus, and others.
Do you like to find out more? Talk to us. - We would be happy to arrange a meeting, or a seminar appointment.

